Web chat, chatbots, virtual assistants, virtual
agents, conversational AI - as
with so much in the world of AI, there is disagreement about definitions. In this
case, it’s better to focus on the functionality and ‘intelligence’ powering it,
rather than the phrase in itself.
What's in a name?
AI for customer contact is currently best
known for chatbots, applications that run automated tasks and simulate
conversation with the customers. It may be given a human avatar and personality
characteristics, and includes natural language processing, dialogue control,
access to knowledge bases and a visual appearance that can change depending on
who it is talking to, and the subject of the conversation. AI Chatbots are often
found in the web chat channel, but the functionality can be used in any other
digital channel, such as social media, email or even voice self-service.
Chatbots are not
always fully-automated or AI-enabled, and may in fact be a glorified FAQ
interface, lacking ‘understanding’ and simply searching through keywords.
However, some use natural language processing and can ask questions to
understand customer intent and improve the accuracy of the output, and may also
use machine learning to improve future outcomes.
Virtual assistants are
not dedicated to a single task (such as customer service), and can assist in
numerous ways such as taking notes, carrying out web research, setting alarms,
communicating with smart devices, etc.
Both chatbots and virtual
assistants are conversational interfaces, but the level of AI involved can
differ greatly.
Web Chat Takes Too Long
Perhaps the most obvious potential use of AI in the customer contact environment is in handling digital enquiries, where
live chats generally take far longer than phone calls (due to agent
multitasking, and typing time) and some email response rates can still be
measured in days.
As the cost of web
chat is broadly similar to other channels such as email, voice and social
media, there is considerable room for increasing efficiencies and lowering
costs.
Web chat automation
has grown in 2018, mainly as a result of initial handling by automated chat
bots which may then hand off to live agents where appropriate. The channel is increasingly popular, especially with the younger generation of customers.
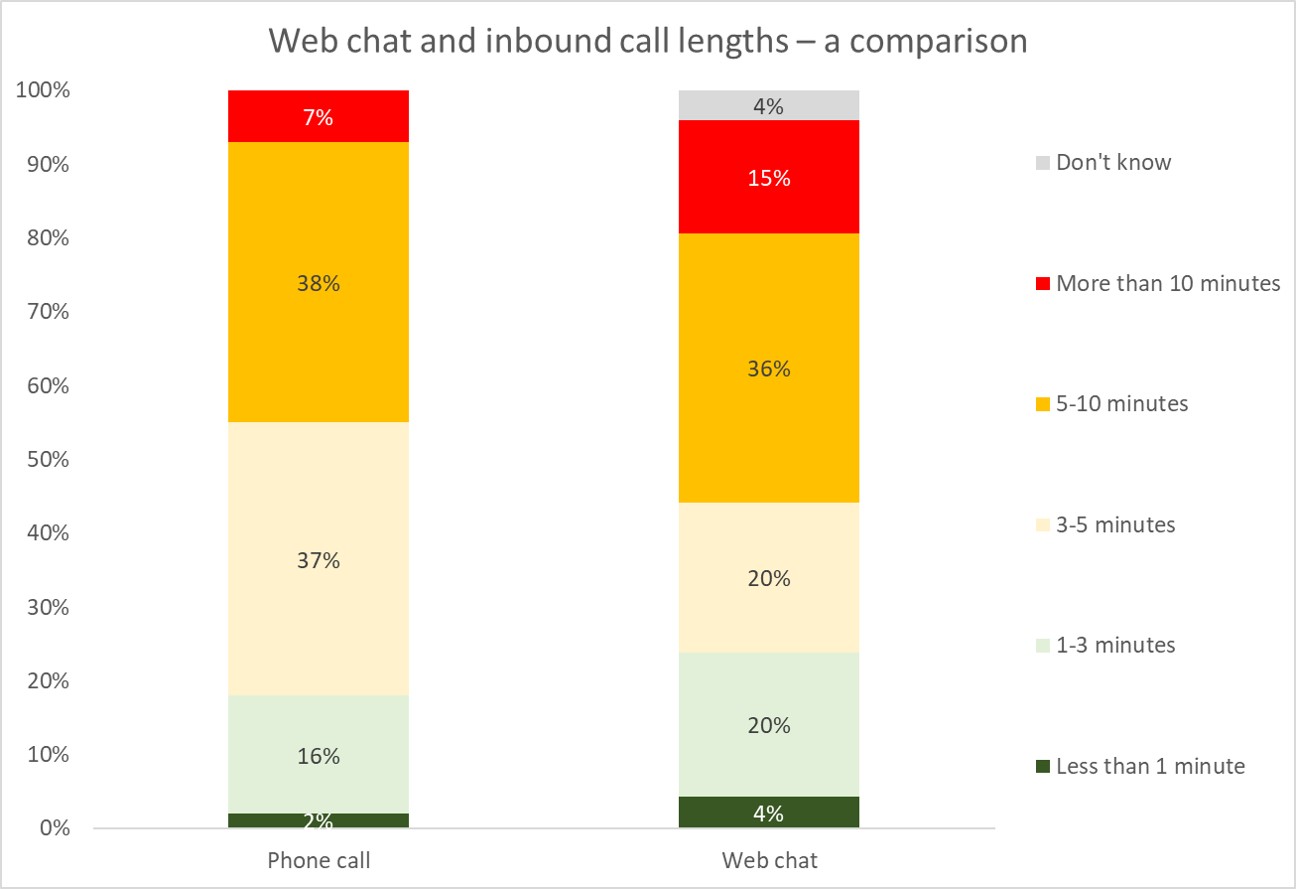
Further comparing the
experience of web chats with telephone calls, surveys find that 52% of web
chats take longer than 3 minutes to complete fully, as agent multi-tasking and
the time taken to type differs from the experience of handling a phone call.
Some customers may
experience a shorter overall length of interaction over web chat: 24% of web
chats are handled in less than 3 minutes, compared to only 16% of phone calls,
almost certainly due to the average complexity of phone queries being greater
than other channels. A lot will depend on the complexity of the query.
From Web Chat to Chatbots
The most sophisticated
chatbots or virtual agents encourage the visitor to engage with them using
natural language, rather than keywords. The virtual agent will parse, analyse
and search for the answer which is deemed to be most suitable, returning this to
the customer instantly. Many virtual agent applications will allow customers to
give all sorts of information in any order, and either work with what it has
been given, or ask the user for more detail about what they actually meant.
Having been unconsciously trained over the years to provide their queries in a
way which standard search functionality is more likely to be able to handle
(for example, a couple of quite specific keywords), customers must be
encouraged and educated to use natural language queries in order for virtual
agents to be able to deliver to their full potential.
The virtual agent
application is different from standard search functionality, ignoring bad
punctuation or grammar, and using longer phrases rather than just searching on
keywords. Sophisticated AI applications attempt to look for the actual intent
behind the customer’s question, trying to deliver a single correct answer (or
at least a relatively small number of possible answers), rather than a list of
dozens of potential answers contained in documents which may happen to contain
some of the keywords that the customer has used. The virtual agent application
may also try to exceed its brief by providing a list of related questions and
answers to the original question, as it is well known that one question can
lead to another. Solution providers and users train the system to pattern-match
the right words or association of words with the correct result: the
application, unlike older forms of web search techniques, does not simply guess
what the customer wants, or how they will express themselves. Through
‘listening’ to what the customers actually say - perhaps through a mixture of
large quantities of audio and text – the initial set-up configuration can
achieve a good accuracy rate, which really benefits over time as a positive
feedback loop is established.
When the virtual agent
application has low confidence that it has returned the correct result, it is
able to escalate the customers query seamlessly to a live chat agent, who then
has access to the self-service session history, enabling a greater chance of a
successful resolution without repetition. (It is generally considered best
practice that escalations to real agents are not hidden from customers). The
eventual correct response can be fed back to the automated virtual agent (and
the knowledge base underlying it), which will make it more likely that future
similar requests can be handled successfully through automated agents.
It’s important to
reiterate an earlier point: not all chatbots or virtual agents are powered
through AI and machine learning – many use programmer-defined rules and
scripting in order to retrieve answers from a knowledge base. While these types
of chatbot have their place in tightly-defined situations where there are a
relatively small number of options or answers, businesses should remember that
not all chatbots work the same way.